3. Station Management
This chapter details the core administrative workflows for managing individual environmental stations, from creation and registration to detailed data inspection.
3.1. Registering a New Station
To begin collecting sensor data, a new station must first be registered within the SenCore platform. This process is initiated by clicking the + Add Station button from the Main Dashboard (visible in Figure 2).
This action opens the “Add New Station” modal, as shown in Figure 6. The user must complete the following metadata fields to define the station:
Station Name & Description: A human-readable identifier.
Location: The precise Latitude and Longitude of the station. This can be entered manually, set automatically via the “Use Current Location” button, or selected by clicking a point on the interactive map.
Metadata: Additional fields for comprehensive records, including Elevation (meters), Timezone, Owner, and Notes.
Tags: Keywords that can be added to group, categorize, and filter stations.
Configuration: Toggles to set the station as a “Public Station” (making its data publicly accessible) or to enable “Debug Mode” for diagnostics.
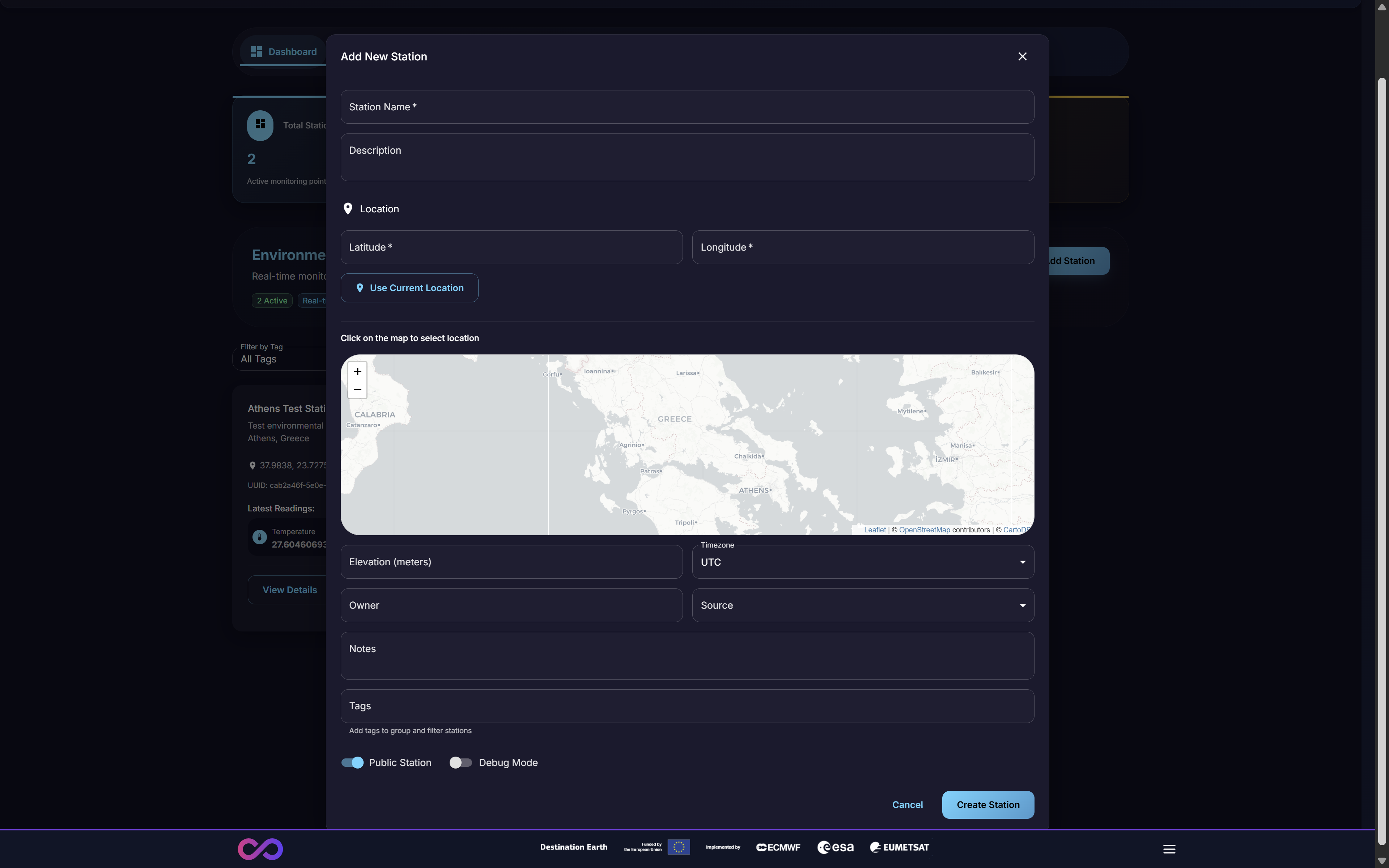
Figure 6: The ‘Add New Station’ modal
A critical step in station registration is selecting the Source (Figure 7). This dropdown menu defines the data ingestion protocol the station will use to communicate with SenCore.
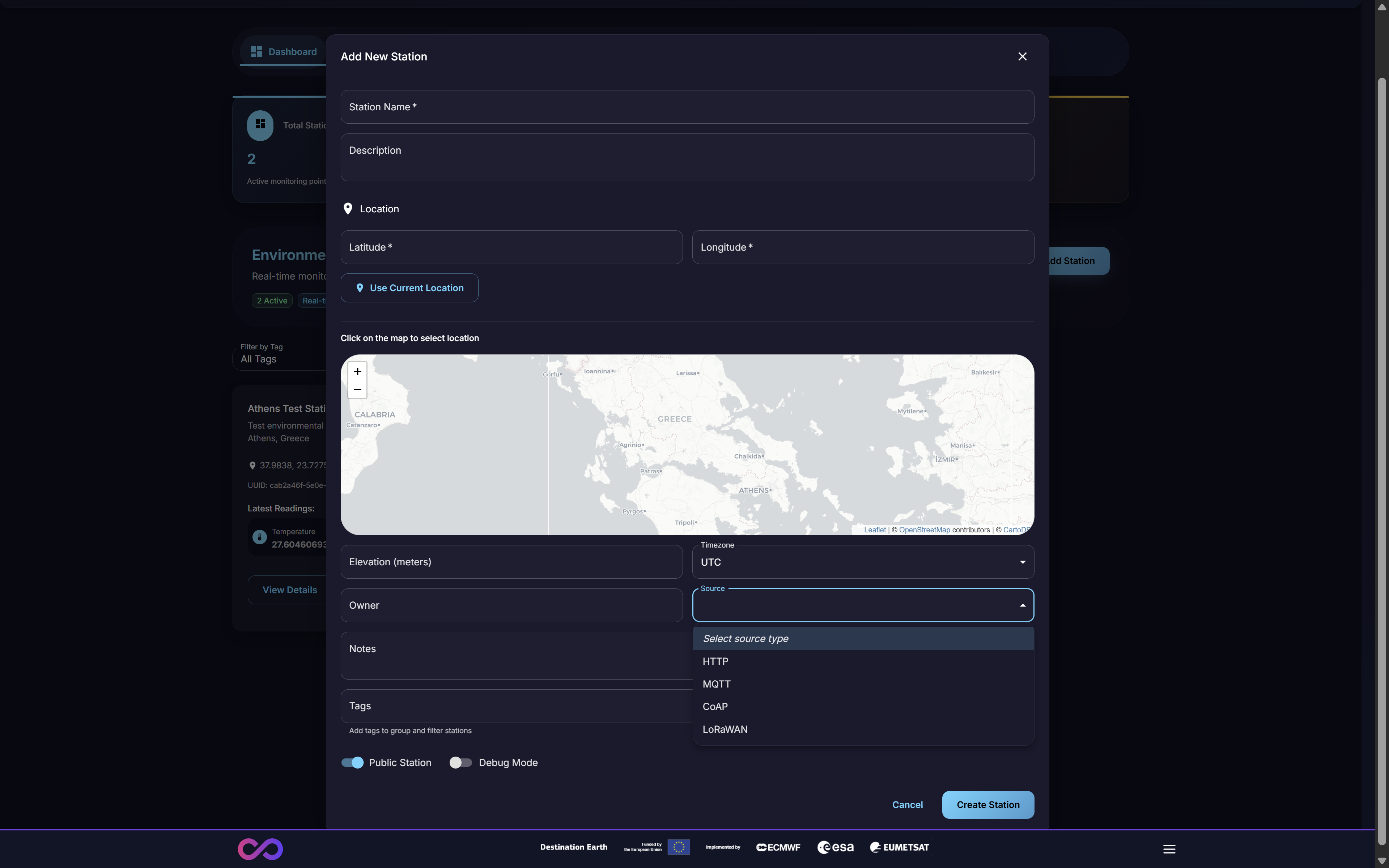
Figure 7: Selecting the ‘Source’ data ingestion protocol
The available protocols are designed for different hardware and network capabilities:
HTTP: Standard web protocol for RESTful API integration
MQTT: Lightweight messaging protocol for IoT devices
CoAP: Constrained Application Protocol for resource-constrained devices
LoRaWAN: Long-range, low-power protocol for wide-area networks
After all fields are completed, clicking Create Station will finalize registration and provision the station in the system.
3.2. Viewing Station Details
From the Main Dashboard (Figure 2), clicking the View Details button on any station card opens a multi-tabbed modal (Figure 8). This interface provides comprehensive information and analytical tools for that specific station.
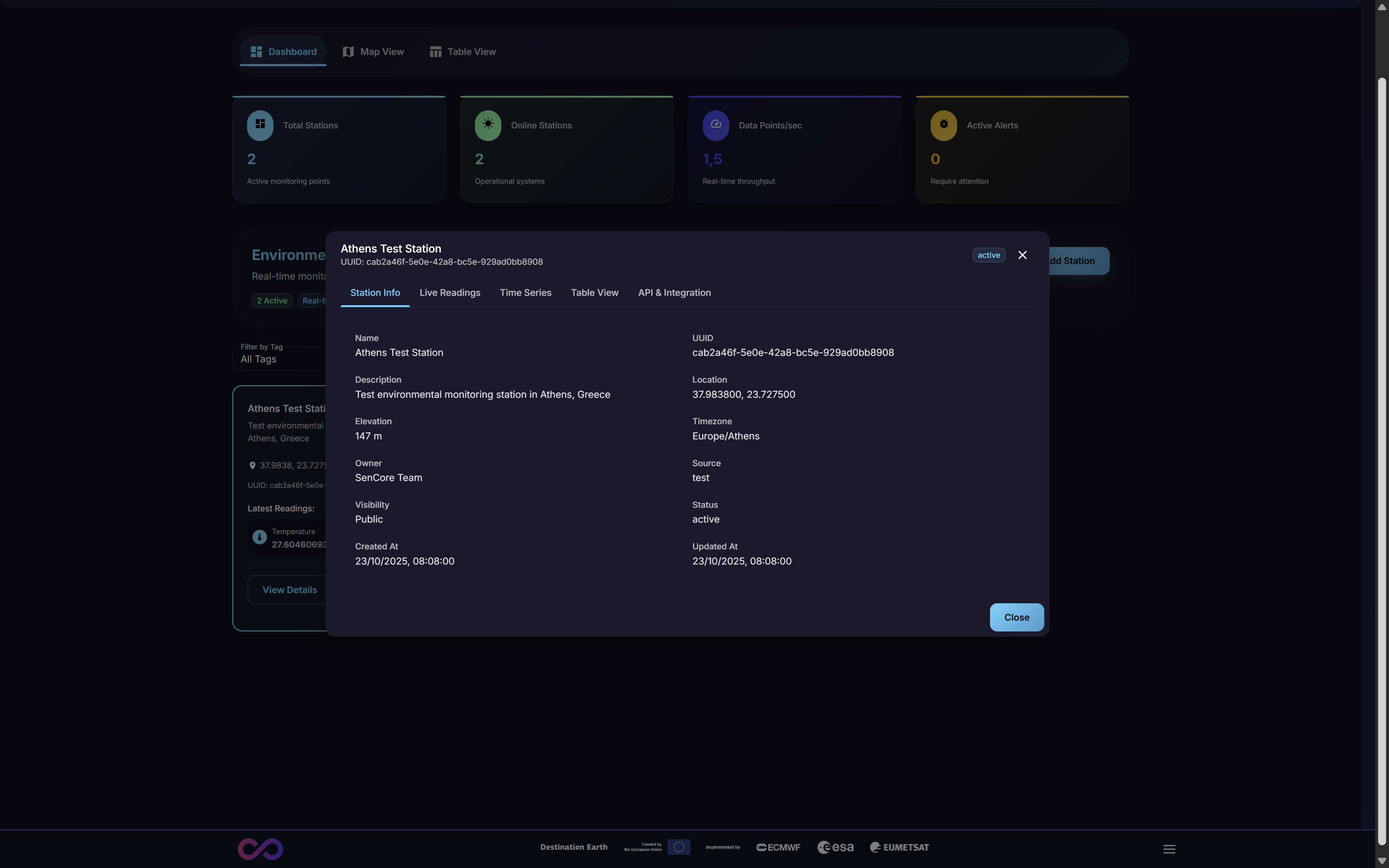
Figure 8: The ‘Station Details’ modal, showing the ‘Station Info’ tab
This modal is organized into five distinct tabs:
3.2.1. Station Info Tab
This tab is active by default (Figure 8) and displays the station’s static, identifying information and metadata. This includes:
Identifiers: Name, UUID, Description
Geospatial: Location (coordinates), Elevation, Timezone
Ownership: Owner, Source (e.g., “test”)
Status: Current Status (e.g., “active”), Visibility (e.g., “Public”)
Timestamps: Created At, Updated At
3.2.2. Live Readings Tab
This tab provides a real-time data feed of the most current sensor readings being transmitted by the station. This view is primarily used for immediate diagnostics, such as confirming that a newly registered station is online and transmitting data as expected.
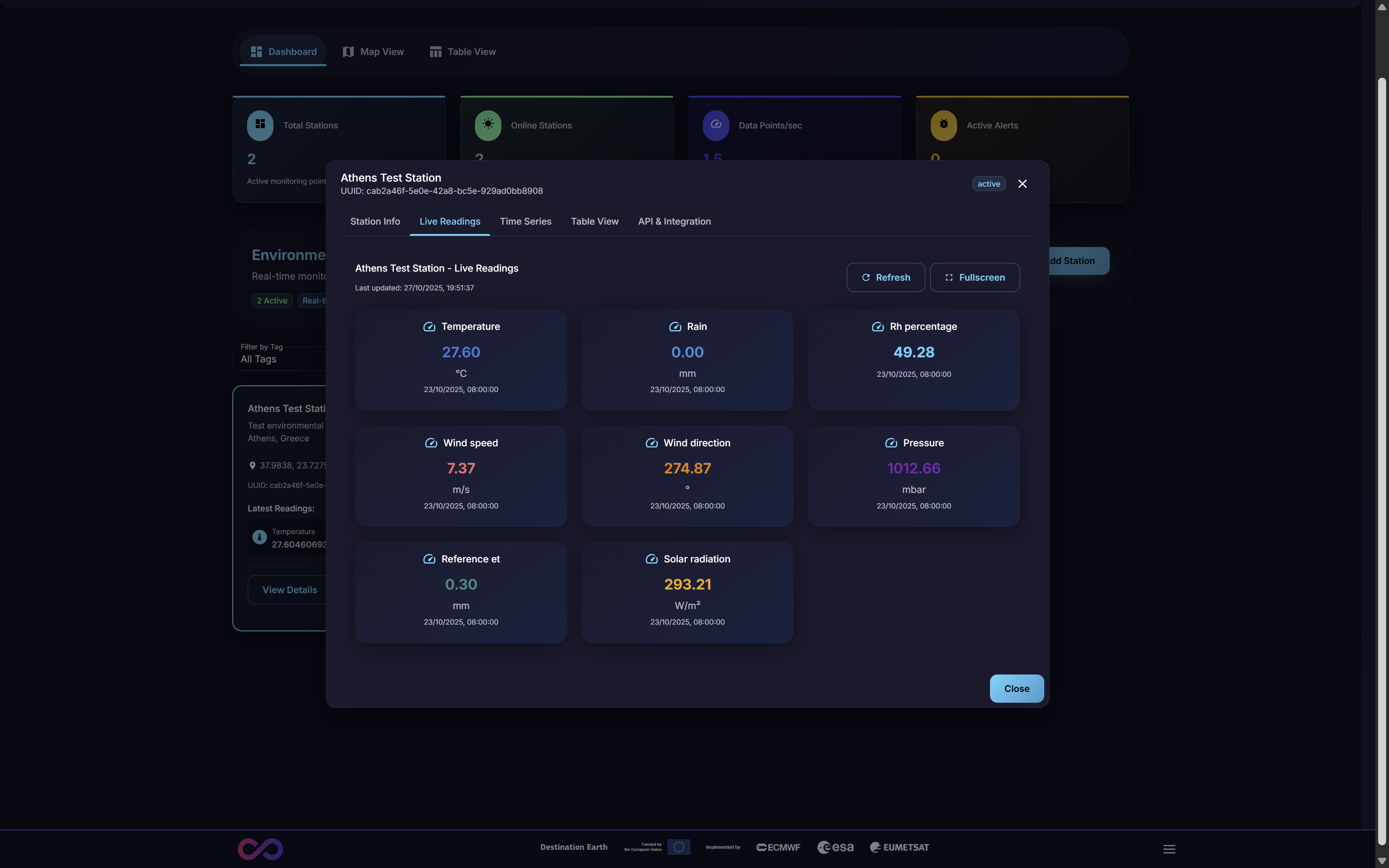
Figure 9: Live Readings Tab showing real-time sensor data
3.2.3. Time Series Tab
This tab opens an interface for plotting and analyzing the station’s historical data trends. Users can select one or more metrics (e.g., Temperature, Humidity) and a specific time range to generate interactive graphs. This is the primary tool for visual analysis of a single station’s past performance and for identifying trends or anomalies over time.
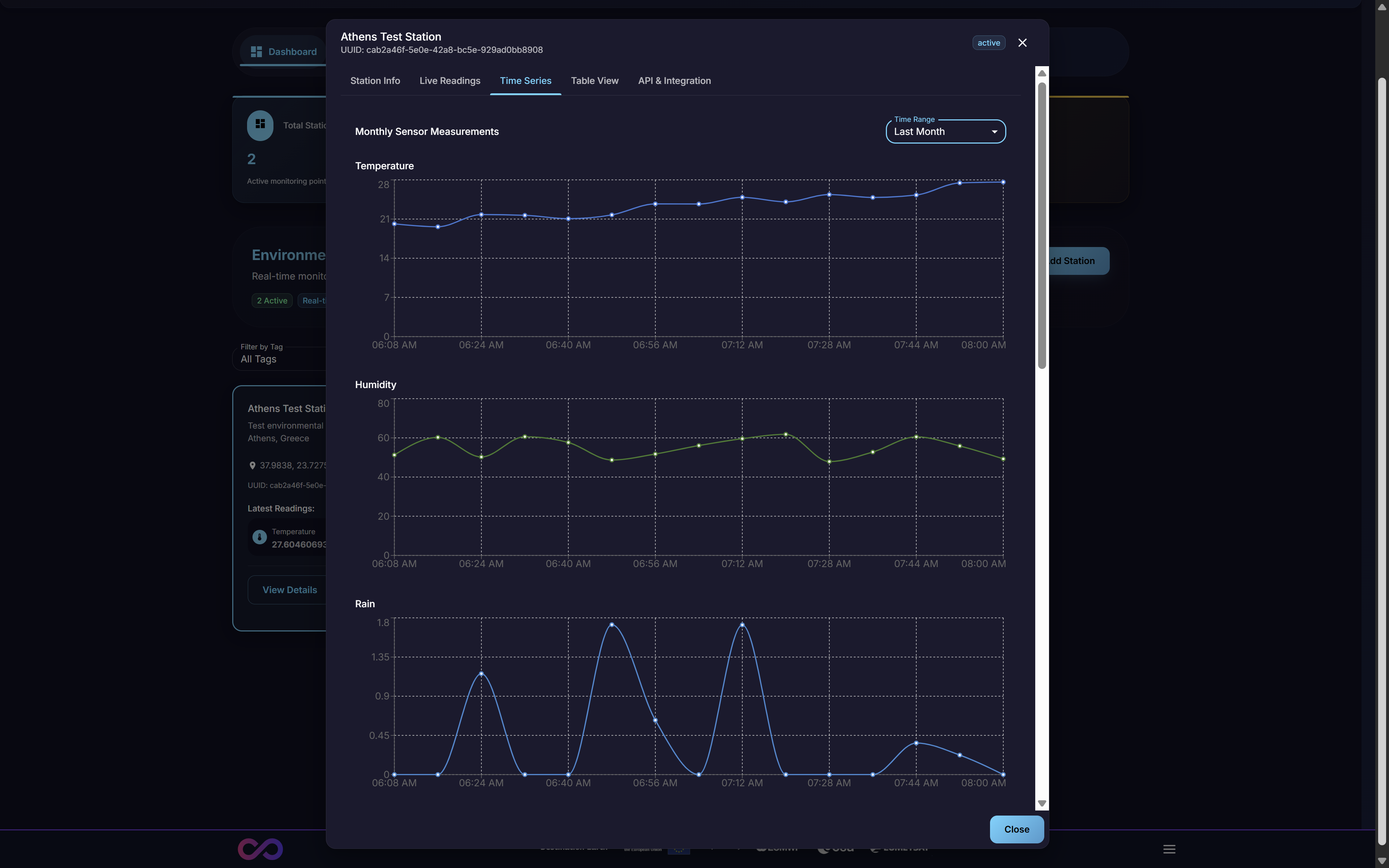
Figure 10: Time Series Tab with historical data visualization
3.2.4. Table View Tab
This tab provides the same tabular data interface as the platform-wide Table View (Section 2.3) but is pre-filtered to show historical data only for the currently selected station. This allows a user to easily view, filter, and search the entire data history for one specific station without the noise of the global dataset, streamlining single-device analysis.
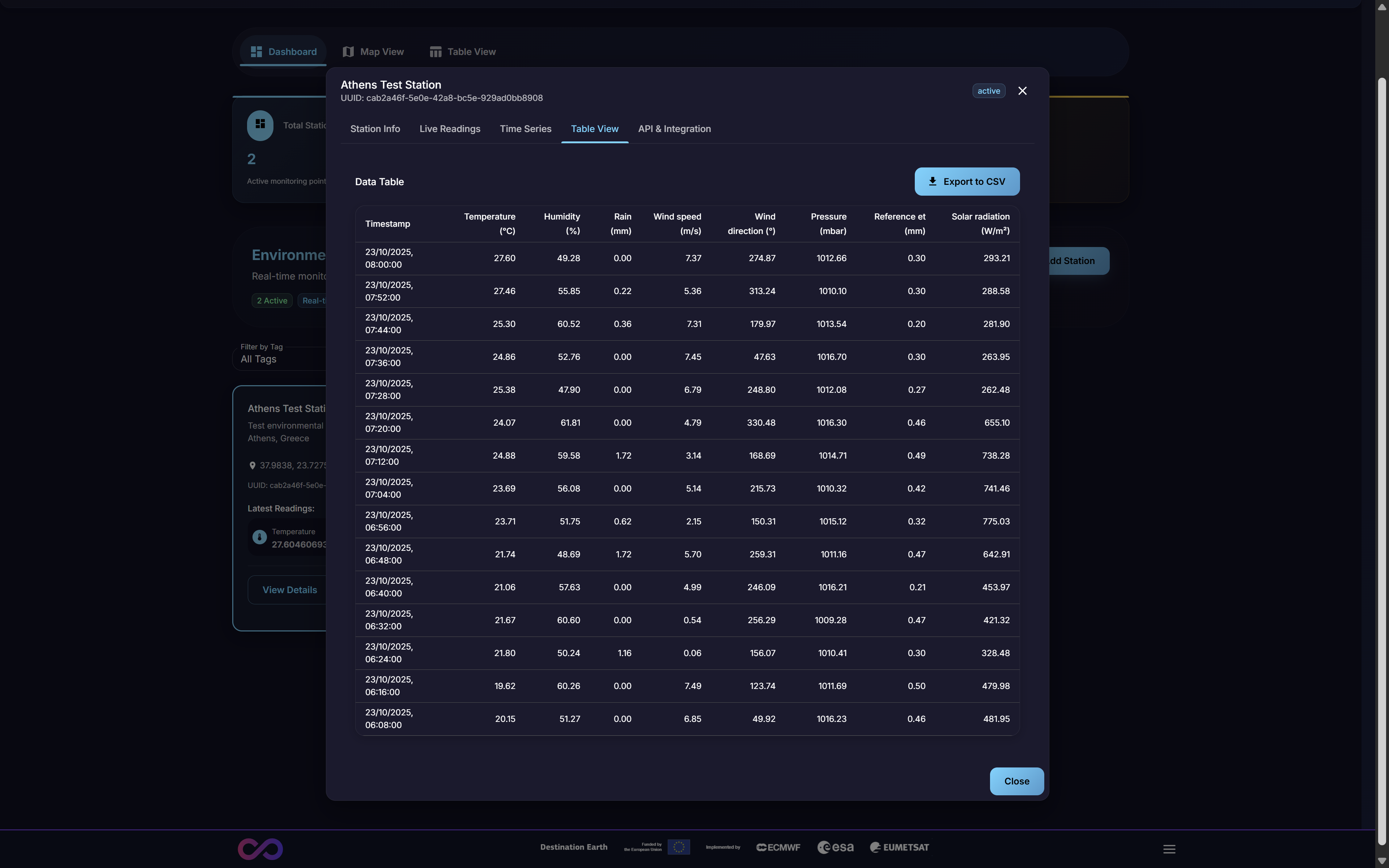
Figure 11: Table View Tab showing station-specific data
3.2.5. API and Integration Tab
This developer-focused tab provides all necessary information for programmatic interaction with the specific station. It is the practical “how-to” guide for implementing the “Multi-Protocol Support” and “RESTful API” features, connecting the abstract “Source” setting (Figure 7) to a concrete integration pathway.
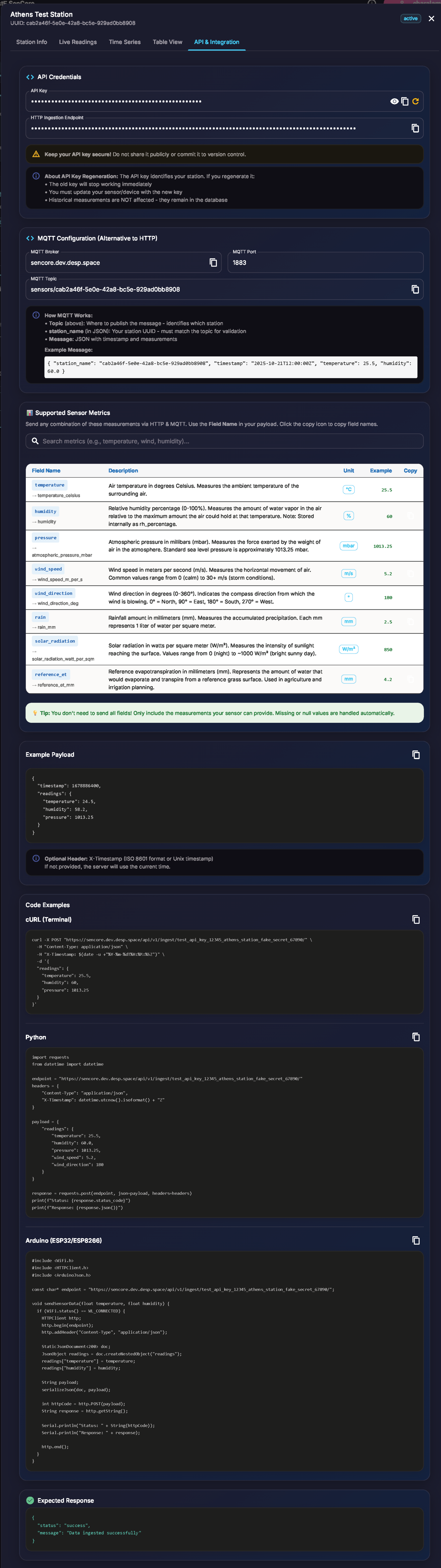
Figure 12: API & Integration Tab with credentials and code examples
This tab provides:
API Credentials: Station-specific authentication tokens or API keys required for secure data submission and retrieval.
Ingestion Endpoints: The specific URL (for HTTP), Topic (for MQTT), or other endpoint information required to send data to this specific station.
Code Snippets: Example code (e.g., cURL, Python) demonstrating how to format and submit data to the endpoint.
Supported Sensor Metrics: A table showing all available measurements with descriptions and units.
API Documentation Link: A direct link to the platform’s full RESTful API documentation (see Appendix).